|
Aspect |
Epidural Anesthesia (EA) |
Spinal Anesthesia (SA) |
|
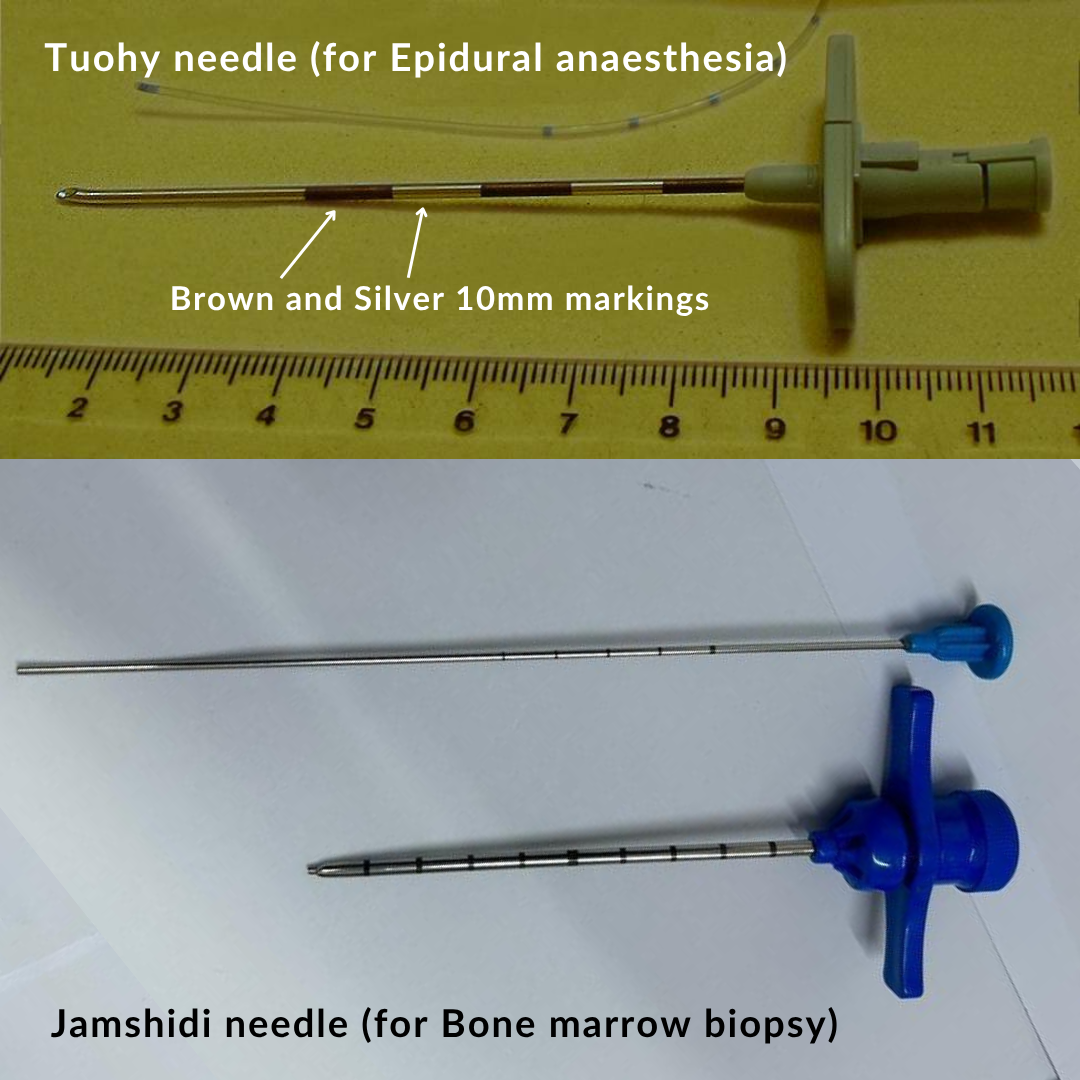
Needle |
Touhy needle |
Spinal needle (Quincke, whitacre, Sprotte tip) |
|
Injection of anesthetic |
into epidural space (b/w ligamentum flavum |
into subarachnoid space (directly into CSF) |
|
Spinal level that can be performed |
Anywhere along the |
Lumbar only (mostly below the L2 vertebra; where spinal cord ends) |
|
Location |
Epidural space, outside the dura mater. |
Subarachnoid space, inside the dura mater. |
|
Drug dose |
Larger dose than SA |
Smaller dose than EA |
|
Onset of Action |
Slower (10-20 minutes). |
Rapid (2-5 minutes). |
|
Duration of block |
Adjustable, prolonged |
Brief, usually 2-4 hours |
|
Redosing |
Possible via inserted catheter |
Not possible |
|
Hypotension & Headache |
No; because there is |
Yes; due to CSF leak |
|
Duration of Effect |
Can be prolonged by continuous |
Typically shorter, single dose. |
|
Control of Dosage |
Adjustable, can be topped up or adjusted as needed. |
Fixed dose, limited to the |
|
Level of Sensation Blocked |
Can be adjusted to block |
Generally results in a more |
|
Common Uses |
Labor and delivery Surgeries of lower body Postoperative pain management |
Cesarean sections |