Relative Risk (RR) is a measure used in epidemiology to determine the strength of association between exposure and disease. It is commonly used in cohort studies.
RR = (Incidence of disease in Exposed group) / (Incidence of disease in Unexposed group)
RR = [a/(a+b)] / [c/(c+d)]
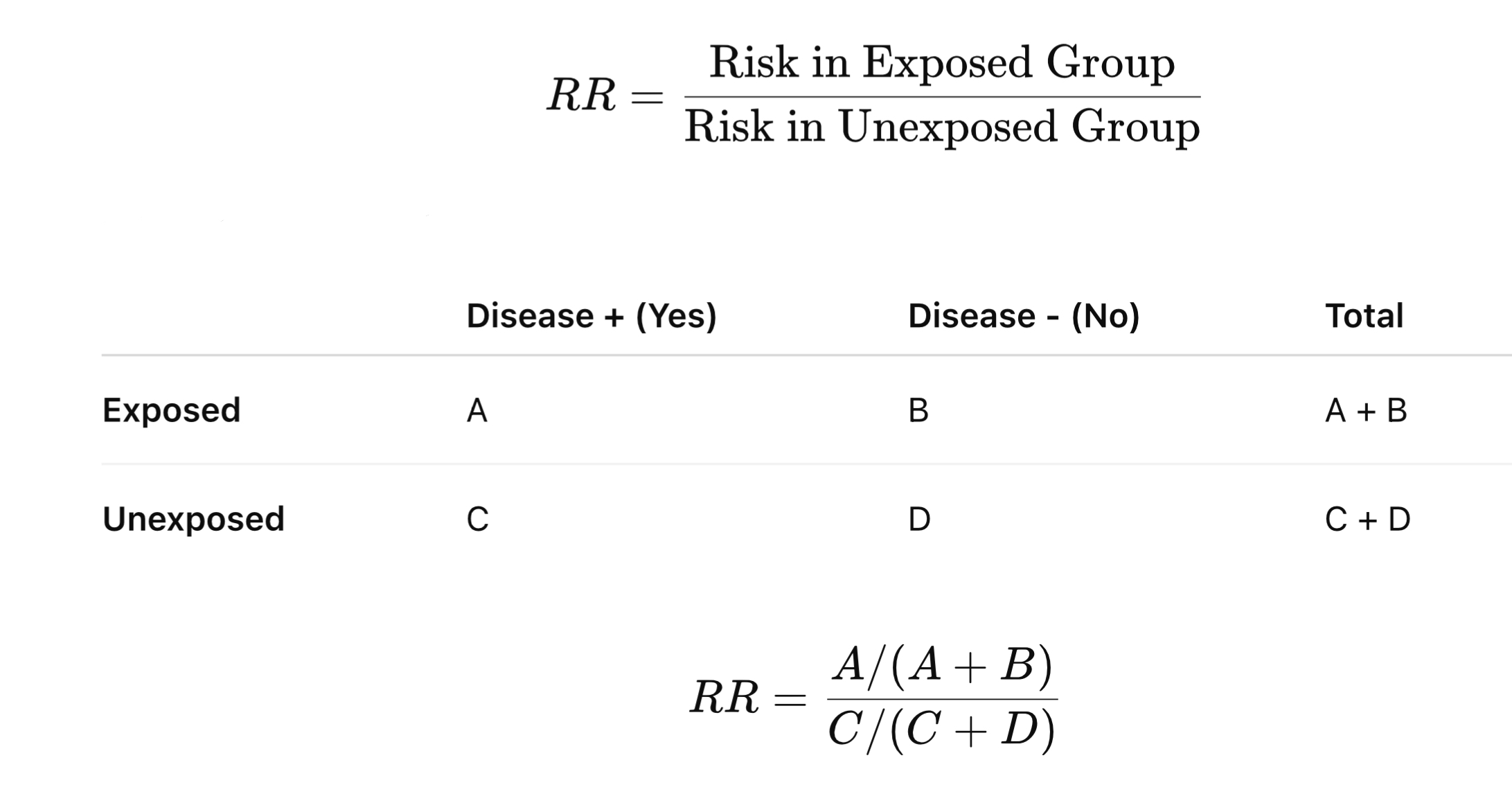
where:
• a = Exposed individuals who develop the disease
• b = Exposed individuals who do not develop the disease
• c = Unexposed individuals who develop the disease
• d = Unexposed individuals who do not develop the disease
|
Interpretation |
Description |
|
RR = 1 |
No association (risk is the same in both groups) |
|
RR > 1 |
Positive association / Risk factor (Exposure increases the risk of disease) |
|
RR < 1 |
Negative (Inverse) association / Protective factor (Exposure is protective against disease) |
|
Case control study |
Cohart study |
|
- Odds ratio |
- Relative risk / Risk ratio - Attributable risk - Population risk ratio |