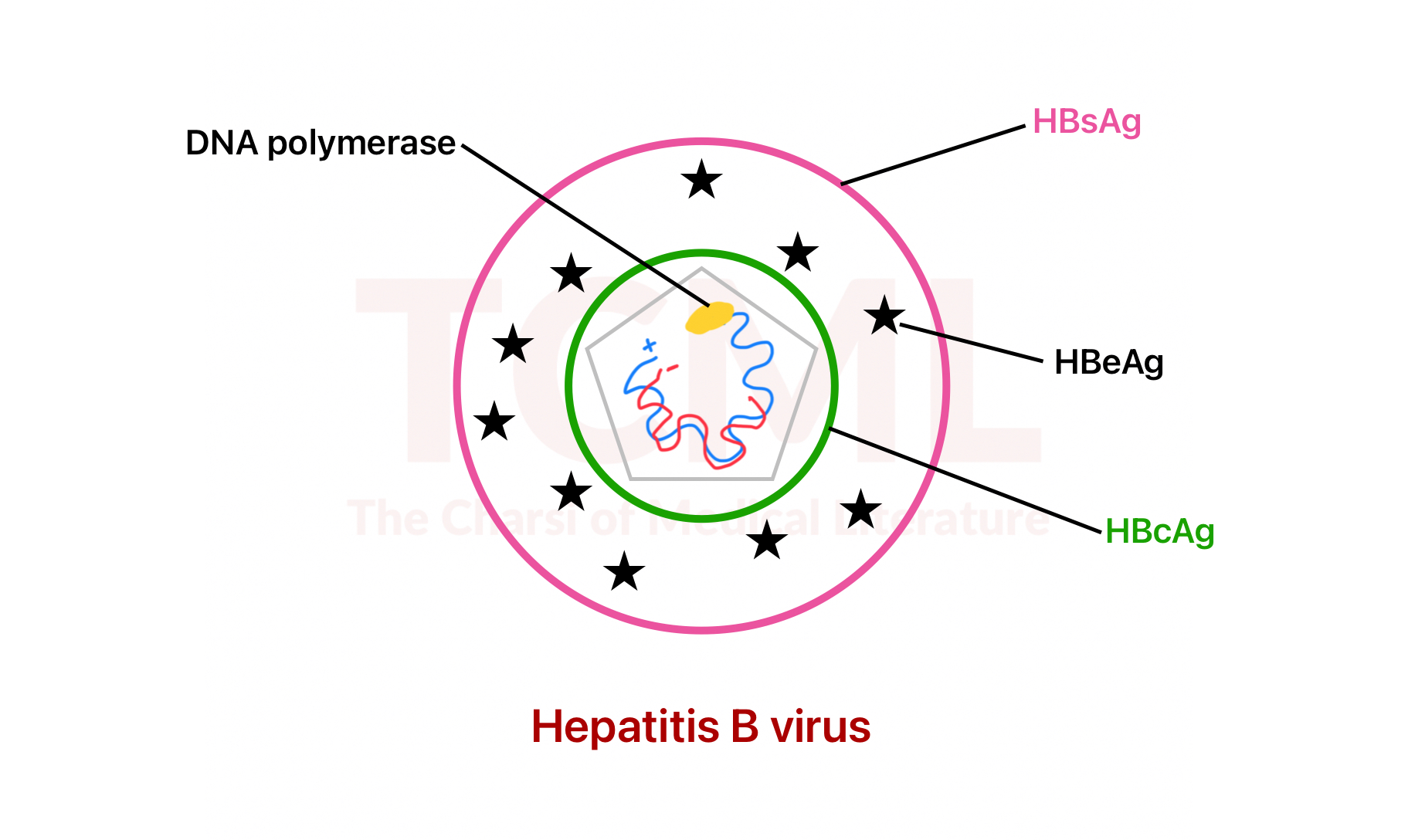
HBV markers and their corresponding antibodies-
|
Ag and Ab |
Diagnosis |
|
HBs Ag (Virus) |
Indicate active infection (Acute & Chronic) |
|
Anti HBs No virus in body (Neutralizing Ab) |
Indicate immunity due to past infection / vaccination |
|
HBe Ag (Increase infectivity) |
Suggests high viral replication and infectivity. (PYQ: UPSC CMS 2023) |
|
Anti HBe (Decrease infectivity) |
Suggests lower infectivity and viral replication. |
|
HBc Ag |
Not detectable in serum |
|
Anti HBc Exposure (Pt expose to virus) |
- IgM Anti HBc: Indicates recent (acute) infection. - IgG Anti HBc: Indicates past or chronic infection. |
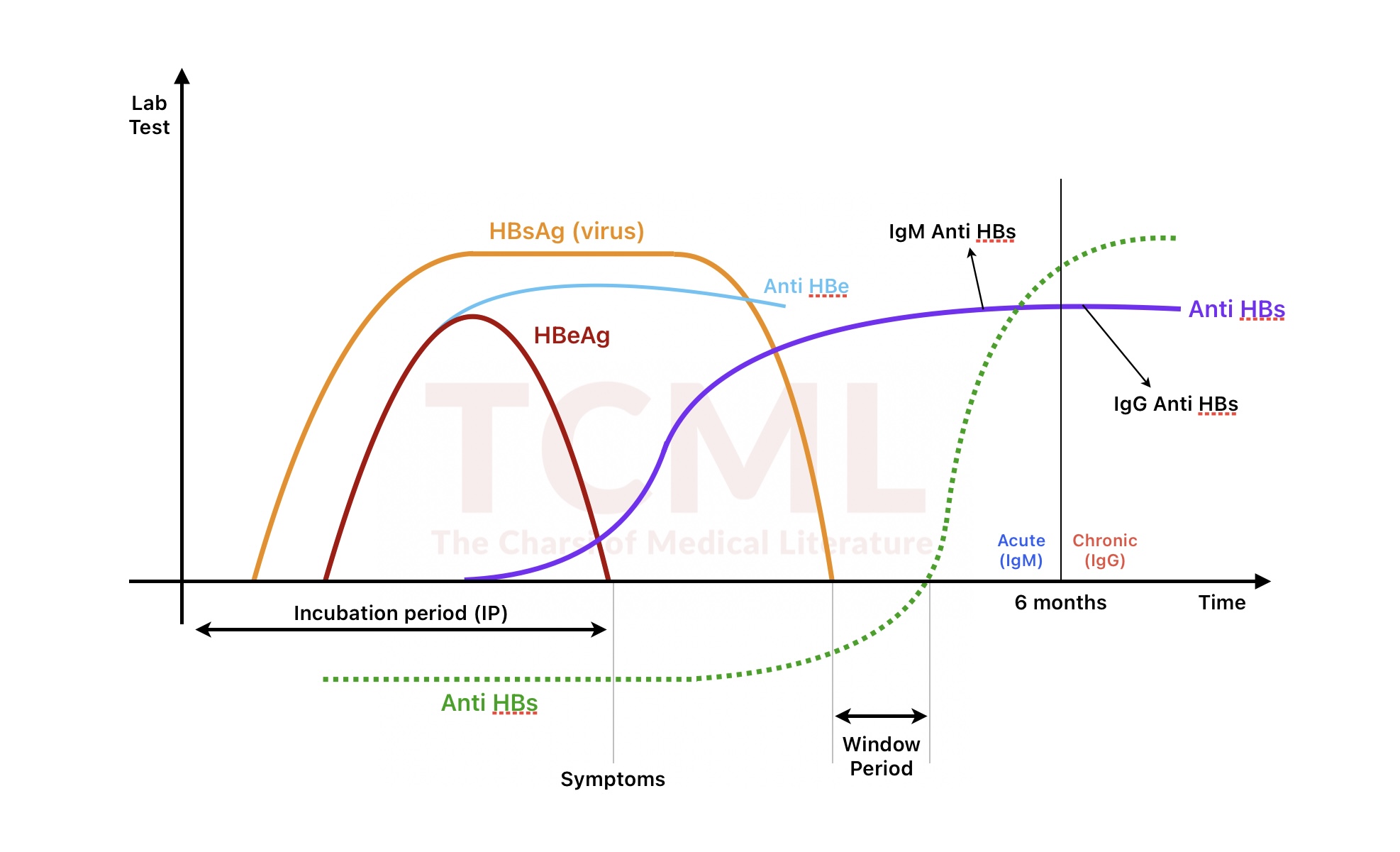
|
Markers |
Interpretation |
|
HBsAg (+) Anti-HBc IgM (+) HBeAg (+/-) |
Acute Hepatitis B |
|
HBsAg (+) Anti-HBc IgG (+) HBeAg (+/-) |
Chronic Hepatitis B |
|
HBsAg (-) Anti-HBc IgG (+) Anti-HBs (+) |
Past infection (Recovered, Immune) |
|
HBsAg (-) Anti-HBc (-) Anti-HBs (+) |
Vaccinated (Immune) |
|
HBsAg (-) Anti-HBc IgG (+) Anti-HBs (-) |
"Isolated anti-HBc" (Possible occult infection, |