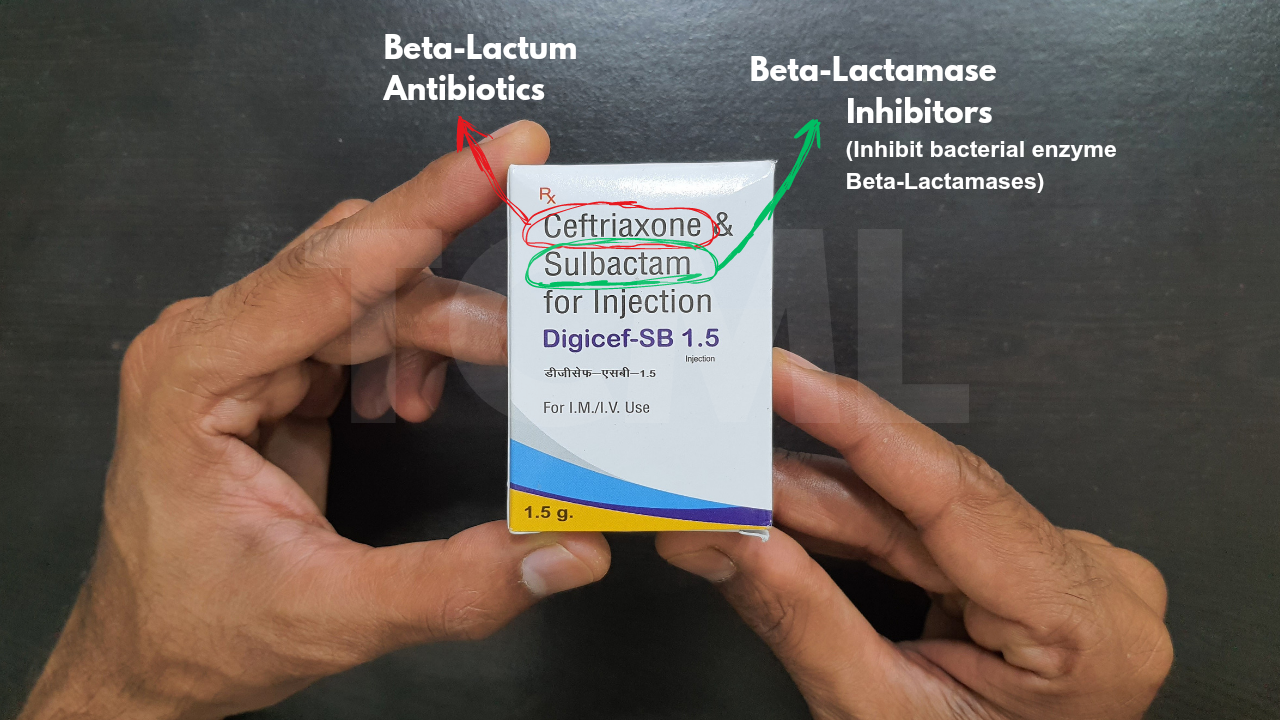
1. Cephalosporins – Ceftriaxone (3rd generation cephalosporin)
2. Penicillins – Piperacillin, Amoxycillin
3. Monobactam – Aztreonam
4. Carbapenems – Meropenem


Beta Lactamase Inhibitor –
• These drugs inhibit the action of beta-lactamase enzymes, which are produced by certain bacteria to inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics (like penicillins and cephalosporins).
• By inhibiting these enzymes, beta-lactamase inhibitors help restore the effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics against resistant bacteria.
• Examples- Clavulanic acid, Sulbactam, Tazobactam.
|
Beta-lactamase inhibitors |
Often combined with |
|
Clavulanic acid |
Amoxicillin |
|
Sulbactam |
Ampicillin |
|
Tazobactam |
Pipercillin |