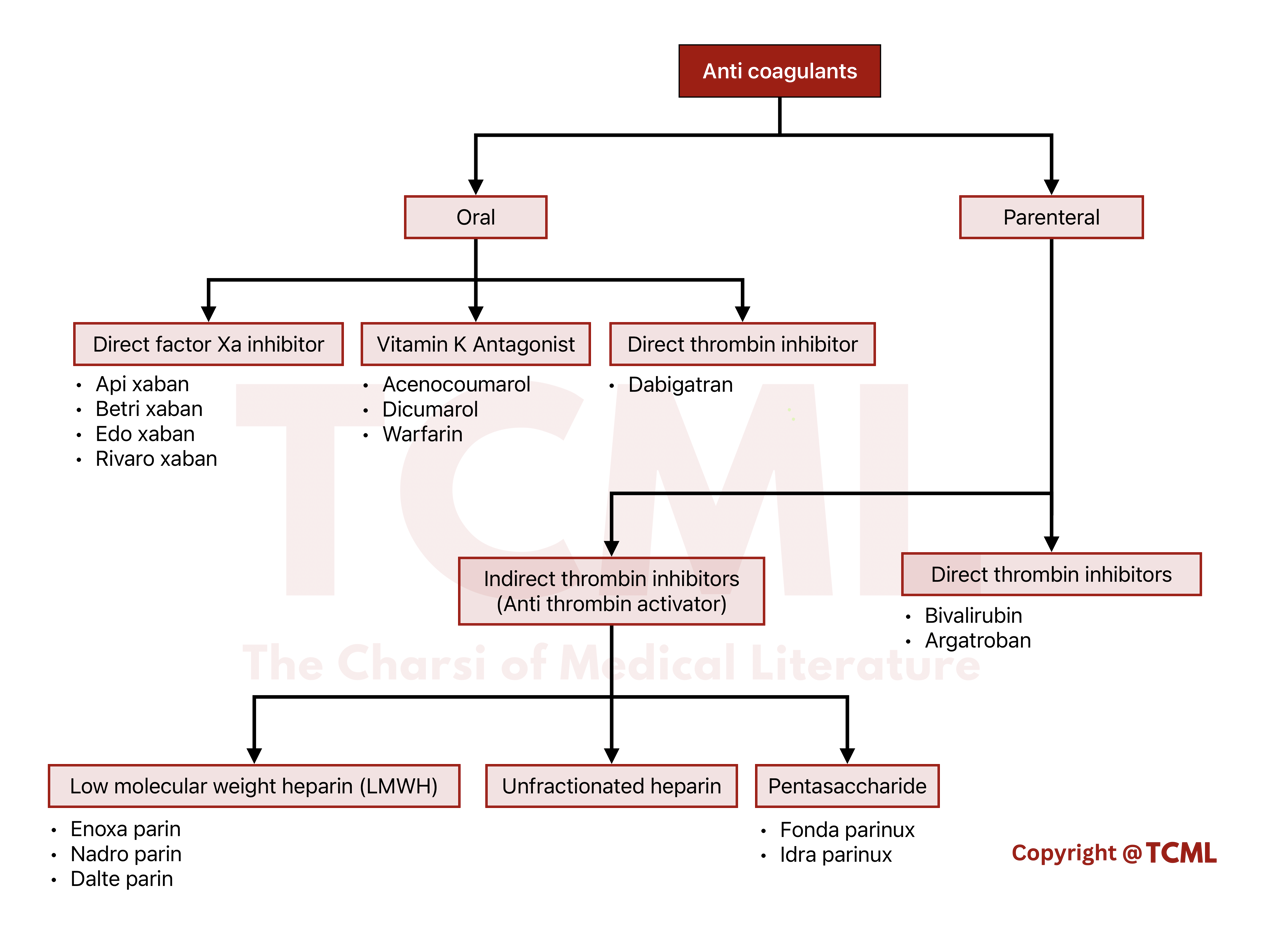
1. Oral anticoagulants
2. Parenteral anticoagulants
|
Oral Anticoagulants |
Drugs |
|
Vitamin K Antagonists (Inhibit synthesis of
2 + 7 = 9, 10 |
• Warfarin (renal safe) • Acenocoumarol (Nicoumalone) • Dicumarol • Bis Hydroxy coumarin
|
|
Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors (Oral drugs that inhibit |
• Rivaroxaban • Apixaban • Edoxaban • Betrixaban |
|
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors(DTIs): Oral |
|
Warfarin-
• Inhibit VKOR-C1 enzyme (example of Competitive inhibition)
• MOA:
- Decrease clotting factor: 2, 7, 9, 10
- Decrease Anticlotting factor: Protein C & S
• Factor 7 (Decrease first / Day 1) → Protein C → → → Factor 2 (decrease in last / Day 5)
• Competitive inhibition effects comes after 5 days so not given in emergency conditions.
• For immediate action add heparin along with warfarin & after 5 days discontinue heparin.
- First 5 days: Warfarin + Heparin
- After 5 days: Warfarin
• S/E- Dermal vascular necrosis (Breast atrophy, Adipose tissue and limb necrosis)
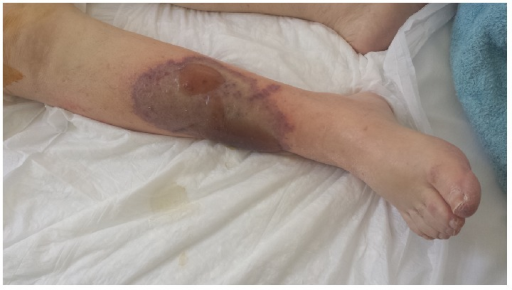 Figure- Warfarin induced necrosis
Figure- Warfarin induced necrosis
|
Parental Anticoagulants |
Drugs |
|
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (DTIs)
|
- Intravenous / Subcutaneous (Never give I/V) - DOC for HIT
- Examples: • Lepirudin • Bivalirudin • Argatroban |
|
Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors (Act via Antithrombin III) |
HMWH / Un-fractionated heparins- • Heparin
LMWH / Fractionated heparins- • Enoxaparin • Dalteparin • Nadroparin
ULMWH / Synthetic heparin • Fondaparinux • Idraparinux |
HIT- Heparin induced thrombocytopenia
HMWH- High Molecular Weight Heparins
LMWH- Low Molecular Weight Heparins
ULMWH- Ultra Low Molecular Weight Heparins